Smartphone users and mobile apps have grown tremendously over the past few years, with more businesses and individuals seeking to create innovative solutions to meet the needs of their customers.
From social media and gaming to banking, healthcare and many other industries, digitalization is everywhere and with it, relevant apps are penetrating with the demand for mobile apps that’s ever been greater. Also, there has been a surge in the number of app ideas. Within the saturated market, it’s important to find out about how to patent an idea for an app.
This also fueled the competition as many app developers or even the best mobile app development company are faced with the challenge of protecting their inventions while ensuring that they remain profitable in the long run. One way to achieve this is through mobile app patents.
Good to Know: The number of mobile app users and downloads has increased significantly over the last few years and shows even greater progress by 2025. Find out here!
What is a Patent?
A patent is a form of intellectual property protection that grants an inventor or owner the exclusive right to use, make, and sell their invention for a specified period and at a predefined cost. In other words, it gives the inventor a monopoly on their invention for a certain period, preventing others from copying, selling, or making use of the invention without permission. In exchange for this exclusive right, the inventor must disclose their invention to the public, enabling others to learn from and improve upon it.
Mobile App Patent Example
Patent rights are granted by governments and vary depending on the jurisdiction in which they are granted. In the United States, for example, patents are granted by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) and typically last for 20 years from the date of filing. Following criteria must be met if your concern is on how to patent an app idea:
- It must be novel and non-obvious
- It must have utility or usefulness
- It must be adequately described and enabled
[Bonus Read: I Have An App Idea, Where Do I Start? (2024 Updated)]
Detailed Steps on How to Patent a Mobile App Idea
Step 1: Research and Check if Your Idea is Patentable
The first step is to make sure that your mobile app idea is patentable. The US Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) has specific criteria that must be met for an invention to be eligible for patent protection. Some of the requirements include:
- Novelty: Your app patent idea must be new and not already disclosed or available in the public domain.
- Non-obviousness: Your patent app idea must not be an obvious modification of an existing invention.
- Utility: Your app idea must have a useful application.
Before investing time and money in the patent process, it’s crucial to do thorough research to ensure that your idea meets these criteria.
Step 2: Conduct a Patent Search
Once you have determined that your app idea is patentable, the next step is to conduct a patent search. This is to ensure that there are no existing patents that cover the same or similar invention as yours. Conducting a patent search will help you identify any potential obstacles to obtaining a patent and help you refine your invention to make it more unique.
The USPTO website provides a free patent search tool that allows you to search for existing app patents. You can also hire a patent attorney or agent to conduct a more comprehensive search.
Step 3: File a Provisional Patent Application
A provisional patent application is a temporary application that provides a filing date for your invention and allows you to use the “patent pending” status. Filing a provisional patent application is not required, but it can be a cost-effective way to protect your invention while you continue to develop it further.
To file a provisional patent application, you need to prepare a written description of your invention, including any drawings or diagrams that can help illustrate your invention. You can file your application online using the USPTO’s Electronic Filing System (EFS).
Step 4: Develop a Detailed App Patent Application
After filing a provisional patent application, the next step is to develop a detailed patent application. This is a more comprehensive application that includes a detailed description of your invention, including how it works, how it’s made, and how it’s used.
It’s essential to include all possible details and variations of your invention to ensure that it’s adequately protected. You may need to hire an app patent attorney or agent to help you draft your patent application.
Step 5: File the Patent Application
Once you have prepared your patent application, it’s time to file it with the USPTO. You can file your application electronically or by mail. There are also fees associated with filing a patent application, and they vary depending on the type of application and the entity filing it.

Step 6: Wait for the Examination Process
After filing your patent application, it will be examined by a patent examiner at the USPTO. The examination process can take several years, and the examiner may request additional information or amendments to your application during this time.
Step 7: Receive a Patent Grant or a Rejection
After the examination process, the USPTO will either grant your patent or reject it. If your app idea patent is granted, you will receive a patent grant, which gives you exclusive rights to your invention for a specified period, typically 20 years from the filing date of your application. You can use your patent to prevent others from making, using, selling, or importing your invention without your permission.
If your patent an app idea application is rejected, you can appeal the decision or make amendments to your application to address the examiner’s concerns. It’s crucial to work closely with your patent attorney or agent during this process to ensure that you are taking the necessary steps to protect your invention.
Step 8: Maintain Your Patent
Once you have obtained your patent, you need to maintain it to ensure that it remains valid. You will need to pay maintenance fees to the USPTO to keep your patent in force. Failure to pay these fees can result in the patent expiring and losing its protection.
It’s also essential to monitor the marketplace for any potential infringement of your patent. If you believe that someone is infringing on your patent, you can take legal action to protect your rights.
Can You Patent an App & Why it’s Important
To patent an app idea is important for several reasons, including the following:
Patenting provides legal protection to inventors and businesses by granting them exclusive rights to their inventions. This means that others cannot make, use, sell, or import the invention without permission. If someone does infringe on a patent app idea, the patent holder can take legal action and seek damages or an injunction to stop the infringement.
Patenting gives inventors and businesses a competitive advantage by allowing them to differentiate themselves from their competitors. By having exclusive rights to an invention, a company can prevent others from producing the same product or using the same technology. This can lead to increased market share and profits.
Patents for apps also create licensing opportunities for inventors and businesses. By licensing their patent to others, they can generate additional revenue streams and expand their market reach. Licensing can also lead to collaboration and partnership opportunities, which can be beneficial for both parties.

It can encourage innovation by providing inventors and businesses with a financial incentive to develop new and innovative products, processes, and technologies. App patents can also facilitate the dissemination of knowledge and ideas by requiring inventors to disclose their invention to the public. This can lead to further innovation and advancements in technology.
Patenting increases the value of a company’s assets. Patents are considered valuable assets and can be bought, sold, or used as collateral. Having a strong patent portfolio can make a company more attractive to investors and potential buyers.
How to Obtain a Mobile App Patent
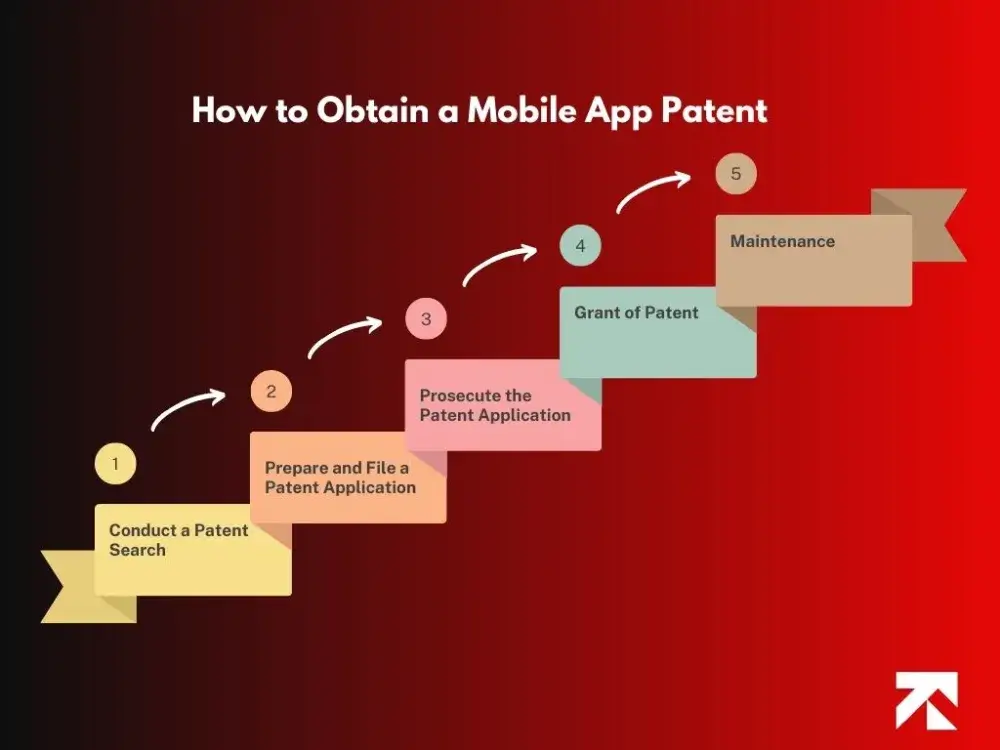
Obtaining a patent can be a complex and time-consuming process. The following steps are generally involved:
-
Conduct a Patent Search
Before applying for an app patent, it’s important to conduct a patent search to ensure that the invention is novel and non-obvious. This involves searching existing patents and other publications to determine whether a similar invention already exists.
-
Prepare and File a Patent Application
Once it has been determined that the invention is novel and non-obvious, a patent application must be prepared and filed with the appropriate patent office. The application should include a detailed description of the invention, including how it works and its unique features.
-
Prosecute the Patent Application
After the patent application has been filed, it will undergo examination by the patent office. The examiner will review the application to determine whether the invention meets the requirements for patentability.
-
Grant of Patent
If the patent office determines that the invention meets the requirements for patentability, a patent will be granted. The patent will provide the inventor with the exclusive right to use, make, and sell the invention for a specified period.
-
Maintenance
After the patent has been granted, the inventor must maintain it by paying periodic maintenance fees to the patent office. Failure to pay these fees can result in the patent becoming invalid. Here, it’s possible you may be interested in knowing about how much does an app design cost to streamline the entire process from the start and avoid any ambiguity.
Different Types of Patenting Mobile Applications
In the context of mobile applications, a patent can protect the functionality, features, and processes that make the app patent idea unique.
Utility patents are the most common type of patents granted for mobile applications. These protect the functional aspects of an invention, including its processes, machines, and compositions of matter. In the case of mobile applications, utility patents can protect the software code, algorithms, and processes used in the app.
To obtain a utility patent, the app developer or app development company must demonstrate that the invention is novel, non-obvious, and useful. Novelty means that the invention must not have been disclosed or made public before the filing date of the patent application. Non-obvious is for the invention not being obvious to someone having ordinary skill in the relevant field, meaning it has to be professional. Usefulness means that the invention must have a practical application.
Design patents protect the ornamental aspects of an invention, including its shape, configuration, and surface ornamentation. In the context of mobile applications, design patents can protect the visual appearance and graphical user interface (GUI) of the app.
To obtain a design patent, the inventor or ideator must demonstrate that the design is original and ornamental. Original means that the design must not be copied from any other source. Ornamental means that the design is aesthetically pleasing and has a unique visual appearance.
Plant patents are granted for the invention or discovery of a new plant variety. While plant patents are not typically relevant to mobile applications, they may apply to apps that deal with plant cultivation or related processes.
Provisional patents are temporary patents that provide the inventor with an early filing date. These are often used to secure the owner’s invention before completion of the development process. A provisional patent application allows the developer to claim “patent pending” status and provides them with a year to file a non-provisional patent application.
To obtain a provisional patent, the app developer or company must provide a detailed description of the invention, including any drawings or diagrams. The provisional patent application does not require claims or formal patent language.
International patents are granted for the protection of inventions in multiple countries. International patents can be obtained through the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT), which provides a centralized application process for multiple countries.
To obtain an international patent, the app developer must file a PCT application and designate the countries where they wish to obtain patent protection. The PCT application is examined by the International Searching Authority, which provides a written opinion on the patentability of the invention.
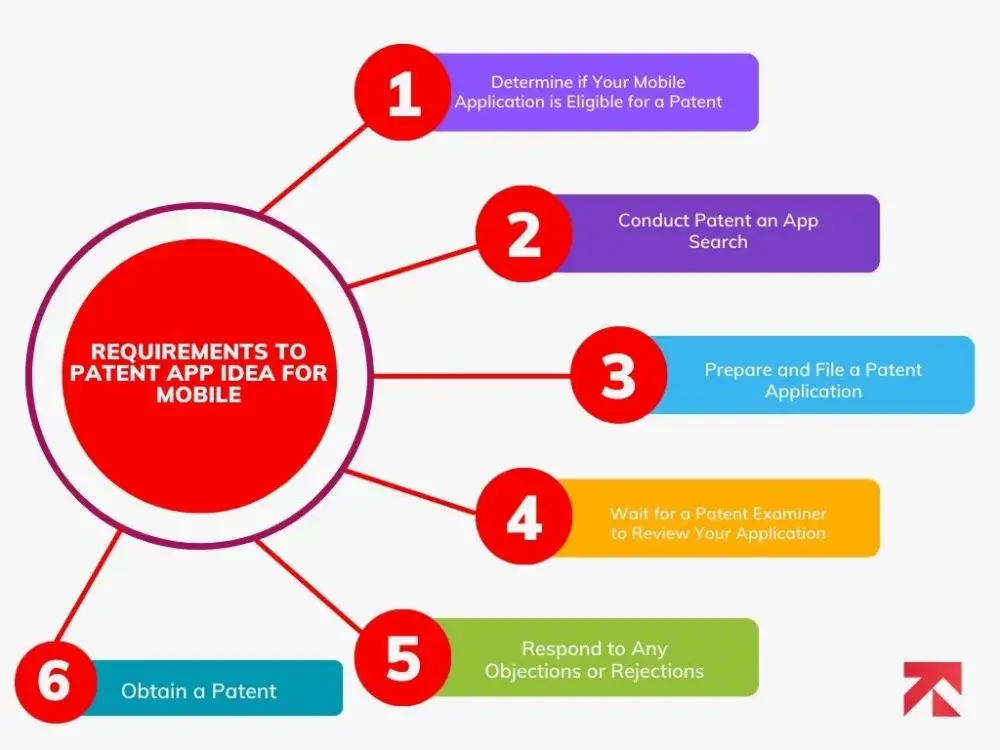
Requirements to Patent App Idea for Mobile
-
Determine if Your Mobile Application is Eligible for a Patent
Before applying for a mobile app idea patenting, you need to ensure that your mobile application is eligible for a patent. The mobile application should be useful in the actual industrial environment. This means that the mobile application should be new and not obvious to someone with average skill in the industry. In addition, it should have a practical use.
-
Conduct Patent an App Search
After determining the eligibility of your mobile application for a patent, you need to conduct a patent search. This will help you identify if there are any existing patents that cover similar technology or features. A patent search can be conducted using various patent databases, including the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) database, European Patent Office (EPO) database, and Google Patents.
-
Prepare and File a Patent Application
After searching for a mobile app idea to patent, you need to prepare and file a patent application with the relevant patent office. In the United States, you can file a patent application with the USPTO, while in Europe, you can file a patent application with the EPO. The patent application should include a detailed description of the mobile application, including its features, functionality, and unique aspects. The patent application should also include drawings and diagrams to help explain the mobile application’s design.
-
Wait for a Patent Examiner to Review Your Application
After filing a patent application, a patent examiner will review your application to ensure that it meets the eligibility criteria for a patent. The patent analyst will conduct a thorough examination of your mobile application and compare it to existing patents to determine its uniqueness and novelty.
-
Respond to Any Objections or Rejections
If the patent examiner finds any issues with your patent application, they may raise objections or rejections. In such cases, you will need to respond to the objections or rejections and make any necessary changes to your patent application. This process may take several rounds of communication and revisions before the patent is granted.
If the patent analyst approves your patent application, you will receive a patent granting you the exclusive rights to the mobile application. This means that no one can make, use, sell, or import your mobile application without your permission. The patent will also provide you with legal protection if someone infringes on your patent rights.
Cost and Benefits of Patenting a Mobile App
We will examine the cost and benefits of patenting a mobile app, and provide insights into what app developers need to know before filing a patent application. At this point, you might also be interested to know about mobile app development cost for the sake of industrial insight or simply to begin with your own unique mobile product,
Benefits of Patenting a Mobile App
-
Exclusive Rights to the Invention
A mobile app patent gives the inventor exclusive rights to make, use, and sell their invention. This means that no one else can use, make, or sell the patented mobile app without the inventor’s permission, which protects the inventor’s investment and can give them a competitive advantage.
-
Increased Market Share and Revenue
By patenting a mobile app, an inventor can differentiate themselves from competitors and gain market share, which can lead to increased revenue. Patent protection can also help attract investors and potential buyers, as they can see that the mobile app is a valuable asset that is protected by law.
A mobile app patent can also provide licensing opportunities, which can be an additional source of revenue. An inventor can license their patented mobile app to others for a fee or royalty, which can generate income without the need to create a new product.
-
Protection from Infringement
Patenting a mobile app can provide legal protection against infringement, which can occur when someone uses or copies the patented mobile app without the inventor’s permission. If an inventor suspects infringement, they can take legal action against the infringer and potentially receive damages.
Cost of Patenting a Mobile App
The process of obtaining a patent can be time-consuming and expensive. It can take several years to obtain a mobile app patent, and the cost can range from a few hundreds to thousands of dollars, depending on the complexity of the invention and the geographic scope of the patent.
-
Uncertainty of Patentability
There is no guarantee that a mobile app will be granted a patent. The patent office may reject the application if they determine that the invention is not new, useful, or non-obvious. The inventor may need to hire a patent attorney or patent agent to help with the application process, which can add to the overall cost.
-
Disclosure of the Invention
When an inventor files a patent application, they must disclose the details of their invention. This means that the invention becomes public knowledge, which can be a disadvantage if the inventor wants to keep their idea a secret.
A mobile app patent is only valid in the country or region where it is granted. This means that an inventor may need to file separate patent applications in different countries to obtain global protection, which can be costly.
Unlock Your Mobile App Potential
Experience the Power of Professional Mobile App Development
Time it Takes to Patent a Mobile App
Developing a mobile app can be a challenging process, but it is important to protect your intellectual property by obtaining a patent. The time it takes to patent a mobile app can vary depending on various factors such as the complexity of the invention, the number of patent applications being processed by the patent office, and the quality of the patent application. In general, it can take anywhere from one to three years to obtain a patent for a mobile app.
The time it takes to acquire a patent or even the process to get completed varies, but in general, the patenting process can take anywhere from one to three years. It is important to note that the process can take longer if there are any issues with your application or if the patent office is experiencing a backlog of applications.
In addition, it is also important to consider the costs associated with patenting a mobile app idea. Patent applications can be expensive, and the cost can vary depending on the complexity of the invention and the amount of time it takes to prepare the application. It is important to budget for these costs when developing your mobile app.
Legal Alternatives to Patenting a Mobile App
Fortunately, there are several legal alternatives to patenting a mobile app that can be just as effective.
-
Copyrights: How to Copyright an App Idea
A copyright is a legal right that gives the creator of an original work exclusive rights to its use and distribution. Copyright an app idea is a legal protection which applies to all kinds of creative works, including mobile apps. When a developer creates a mobile app, they automatically own the copyright to it. Registering a copyright with the US Copyright Office provides the developer with additional legal protections.
Copyright protection is particularly useful for protecting the code, graphics, and other creative elements of a mobile app. It prevents others from copying or using these elements without permission. Copyright protection also lasts longer than a patent – the duration of a copyright is the life of the creator plus 70 years.
How to trademark an app idea covers all aspects such as symbol, design, word, or phrase that identifies and distinguishes the source of goods or services of one party from those of others. Trademarks protect the branding and marketing of a mobile app, such as its name, logo, and slogan. Registering a trademark with the US Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) provides the developer with additional legal protections.
Trademarks are particularly useful for preventing others from using a similar name or logo that could confuse consumers into thinking that the other app is affiliated with the original app. Trademark protection can also last indefinitely, as long as the mark remains in use and is renewed periodically.
A trade secret is a formula, pattern, process, or information that gives a business a competitive advantage. Trade secrets are not registered with any government agency, and they remain secret as long as the business takes reasonable steps to keep them confidential.
Trade secrets are particularly useful for protecting the underlying algorithms, data structures, and other technical details that make a mobile app unique and valuable. By keeping these details secret, a developer can prevent others from copying the app’s functionality. However, it’s important to note that trade secrets are not foolproof – if someone else independently develops the same information, they can use it without penalty.
-
Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs):
A non-disclosure agreement (NDA) is a legal contract between two parties that outlines confidential information that the parties wish to share with each other for certain purposes, but not to the public. NDAs prevent the recipient from disclosing the confidential information to others without permission.
NDAs are particularly useful for protecting the idea and development process of a mobile app. Before sharing an idea or information with a potential investor or partner, a developer can require them to sign an NDA to ensure that the information remains confidential. However, it’s important to note that NDAs are only enforceable if the recipient violates the agreement – they do not provide any legal protections against independent development or theft of the idea.
Trango Tech’s Recommendations on Patenting a Mobile App
Before applying for an app patent, it is essential to conduct a patent search to ensure that your mobile app is not infringing on existing patents. At Trango Tech, we recommend consulting with a patent attorney to conduct a thorough search of existing patents and trademarks to identify any potential infringements.
-
Identify Patentable Elements
Not all elements of a mobile app are patentable. Trango Tech suggests identifying the patentable elements of your mobile app and focusing on those when applying for a patent. For example, unique features or functionality may be patentable.
-
File a Provisional Patent Application
Trango Tech recommends filing a provisional patent application before submitting a full patent application. A provisional patent application provides a placeholder for your invention, giving you a year to file a full patent application while protecting your rights in the interim.
-
Work with a Patent Attorney
Working with a patent attorney is essential to ensuring that your patent application is completed correctly and to the highest standard. A patent attorney can provide guidance on the patenting process, including conducting a patent search, drafting the patent application, and responding to patent office actions.
-
Be Prepared for the Cost and Time Involved
Patenting a mobile app can be costly and time-consuming. Trango Tech suggests being prepared for the cost and time involved in the process, including patent attorney fees, patent office fees, and ongoing maintenance fees.
Frequently Asked Questions on Mobile App Patent (FAQs)
-
What can be patented in an app idea?
Any novel and non-obvious invention having a useful purpose and potential to generate healthy business can be patented. A few elements covered by a patent may include composition, production process, machine, tool, new plant species, or even an upgrade to an existing invention. All such products and inventions must align with the government guidelines for the patent to be approved.
-
How long does the patent process take?
As per the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO), a patent may take approximately 22 months i.e almost 2-years to get approval following all the legal procedures. As for those who qualify for a priority exam against plant and utility patents also known as Track One, a patent may be approved anywhere between six months to an year.
-
Do I need a patent attorney to file a patent application?
Unless you’re well aware of all the patent rules and regulations, a patent attorney can help you overcome all the challenges and obstacles that might interfere in approval of a patent application. Also, it depends on your budget to hire a patent attorney.
-
How much does it cost to patent an app idea?
Each patent application is unique in its entirety. A typical mobile app patent may cost between $3,000 to $6,000 plus the filing fees charged by USPTO that can be anywhere between $70 to $140.
-
Can I patent an app idea internationally?
By filing a patent application in each country where you wish to safeguard your app against misuse, fraud or copyrights, you can patent it internationally. You can also file an international patent in coordination with the Patent Cooperation Treaty (PCT) which gives protection in multiple countries.
-
How can I ensure that my app idea is kept confidential during the patenting process?
Your patent app idea will remain confidential during the entire process. You can also sign an NDA to make sure it remains safe from public release unless the patent is approved and you have the legal right to reveal it to the users.
-
Is it possible to patent an app idea if I am not a programmer or developer myself?
Yes. You will have to register yourself with the idea before patenting and meet all the legal formalities in order for the process to move forward smoothly.