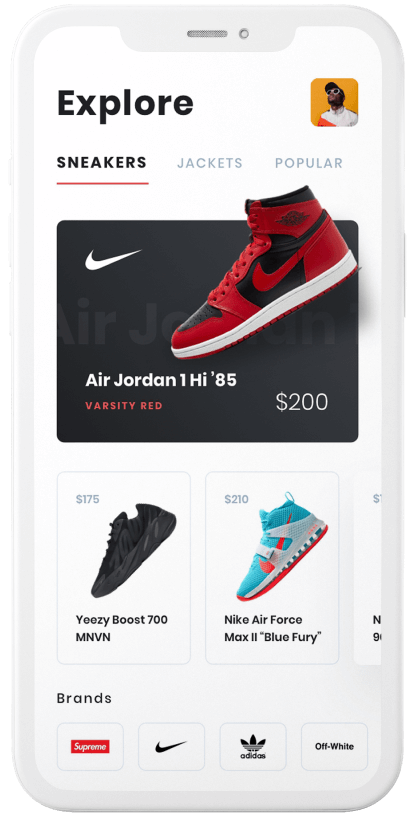
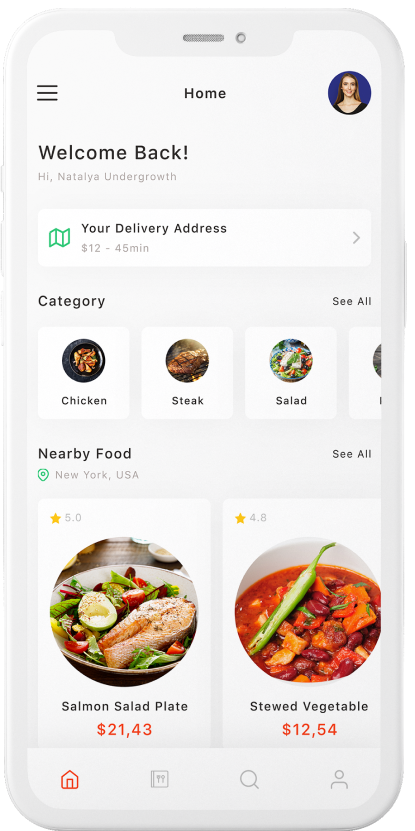
Oracle
Oracle is an RDBMS that helps implement object-oriented features, such as polymorphism, inheritance, and user-defined types. It is the first ever database designed to assist with enterprise grid computing while being flexible and cost-effective. Oracle database uses memory structures and processes to access and manage the database.
MySQL
MySQL is used to create databases for manipulating and storing data while defining the relationship of each table. Developers can make specific requests by typing specific SQL statements on MySQL. In turn, the server application responds with the information requested and makes it appear on the developer’s side.
SQL Server
SQL Server is an RDBMS by Microsoft that assists developers in a wide range of transaction processing, analytics applications, and business intelligence in the corporate IT environment. SQL Server uses Java, C#, R, and Python as the main languages. Five types of SQL Servers mostly used include Enterprise, Web, Standard, Developer, and Express.
MongoDB
MongoDB is a non-relational document database with a flexible data model. It enables developers to store unstructured data, provide full indexing support, and replicate with initiative and rich APIs. MongoDB uses a scale-out architecture that allows developers to store data easily. It uses MongoDB Query Language (MQL), very similar to SQL.