The world has changed drastically in the last 10 years, especially following the aftermath of Covid-19 and a global financial meltdown, forcing people and businesses to adopt new technological trends such as digitization. This is especially true for the healthcare industry which was at the forefront of combating the spread of Covid-19.
With that said, there are a plethora of emerging healthcare trends and technologies that are being adopted by various companies such as Trango Tech, the leading healthcare app development company, to cater the rapid growth of the healthcare industry. According to a report by Forbes, the healthcare industry’s revenue is expected to grow up to $97 billion by 2027. We’ve gone ahead and listed some emerging healthcare trends of 2023.
AI Applications in Healthcare
Talking specifically about the healthcare industry, artificial Intelligence is one of the most booming trends in healthcare technology as it is used in completing activities that would otherwise be completed by patients, doctors, and hospital admin and staff, helping make their lives easier.
Healthcare accounted for about a fifth of total funding in 2021 for the AI sector, one of the industries with the highest growth rates in the world, according to CB Insights. Through machines that can predict, comprehend, learn, and act, AI is reinventing and reviving modern healthcare, whether it’s used to find new connections between genetic codes or to power robots that assist surgeons. Let’s take the example of ‘The pastry AI that learned to fight cancer cells’ to help us better understand the applications and limitless potential of AI.
Big Data Application in Healthcare
Treatment models have altered as a result of our extended lifespans, and many of these changes are largely the result of big data. Since treating any disease at an early stage is easier and less expensive, doctors aim to learn as much as they can about a patient and as early in their life as possible to pick up warning symptoms of serious illness while they are dormant. Prevention is better than cure, and being able to paint a complete picture of someone will allow insurance to offer a customized package. These concepts are reinforced by the use of key performance indicators (KPIs) in healthcare and healthcare data analytics. This is the industry’s attempt to address the siloed issues that a patient’s data has: bits and pieces of it are scattered around and archived in clinics, hospitals, surgeries, and other settings, making it difficult to interact effectively. If utilized efficiently, big data has the potential to add $300 million per annum to the healthcare industry.
VR Applications in Healthcare
Virtual Reality is one of the rising technology trends in healthcare which will allow healthcare professionals and patients to interact with simulated environments designed for medical education (including training in simulative surgery), pain management, or rehabilitation.
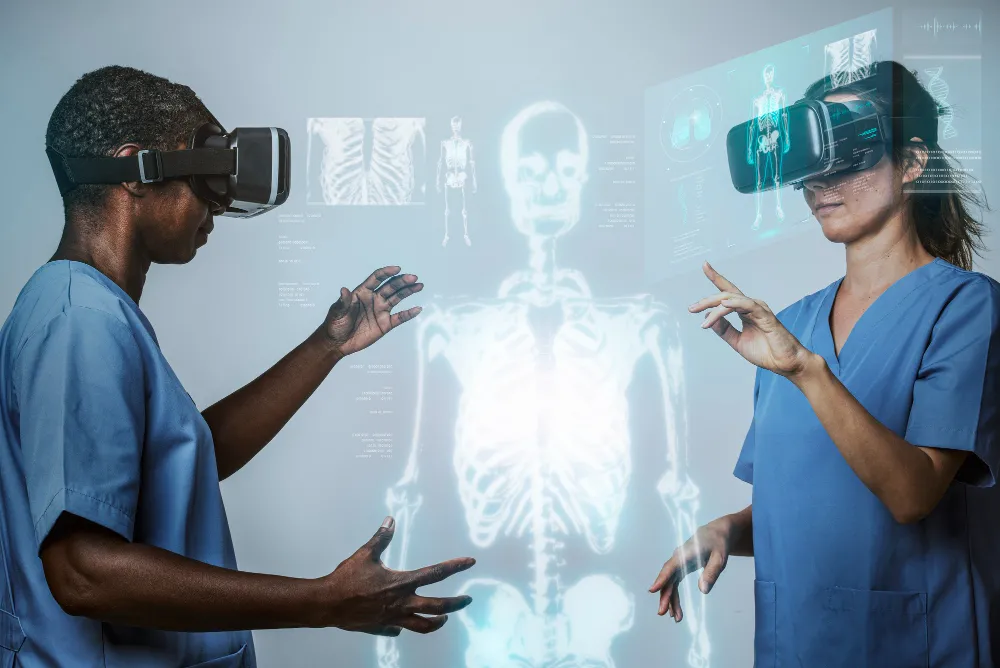

In a report published by Goldman Sachs Global Investment Research, it was stated that healthcare will remain one of the top three leading industries adopting Virtual Reality technology up to 2025.
Now, we’ll talk about the applications of VR in the healthcare industry in detail.
Medical training
Virtual reality (VR) technology can be used to replicate any medical situation, allowing students and staff to respond to it as if it was actually happening. Feedback and a debriefing can be provided to help them identify and learn from their mistakes. Since academic members are not required to be present and VR devices are relatively inexpensive, access is more open-ended and inclusive.
Medical professionals can use VR to visualize the human body’s interior, opening up previously inaccessible spaces. For starters, virtual reality studies of human anatomy have replaced the dissection of cadavers, which was once required of all beginning medical students.
Treatment of patients
With virtual reality, the surgical team can practice their planned intervention and go through the entire treatment, which is helpful for planning complex surgeries like neurosurgery procedures.
This reduces surprises, hence increasing safety. CT, MRI, and ultrasound scans are used to compile the data, which is then supplemented with VR and haptics. When in a surgical setting, the reconstruction resembles the real patient in both appearance and sensation.
In surgical robotics, which rely on a robotic arm that is operated by a human surgeon sitting at a console, VR is also essential. The inside-the-body camera is used by the surgeon to get a view of the area being operated on. However, tactile and sensory input are also crucial during surgery, and virtual reality (VR) may fill in for them in a reasonable way.
Other applications of VR in healthcare are that they can be used to help patients overcome various phobias through a controlled simulation in a safe environment without exposing the patient to risk.
Pain Management
The mind has more power and control over the human body then we can fathom. The ‘rubber hand’ experiment helped showcase a small fraction of it. The same science applies in VR. Immersive Virtual Reality has been successful in helping alleviate pain or rehabilitate patients with severe pain, especially when paired with controlled doses of anesthesia or sedatives.

Robotics Application in Healthcare
In the medical industry, applications of robotics are one of the rising trends in healthcare, revolutionizing how procedures are carried out, speeding supply delivery and sterilization, and allowing professionals to concentrate on interacting and caring for patients. For the creation of medical robots, leading tech companies like Intel provide a wide range of technologically advanced robots, such as surgical-assistance, modular, and autonomous mobile robots.
In order to support medical staff and improve patient care, robots are now deployed in clinical settings in addition to operating rooms. For example, to help reduce exposure to pathogens during the COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals and clinics are using robots for a much wider range of tasks.
Robotics and automation are also used in research labs to automate manual, repetitive, and high-volume tasks so that technicians and scientists can concentrate on more strategic tasks that lead to faster discoveries.
Robotic surgical assistants
Robots used for surgical aid have improved in precision as motion control technologies have developed. With the use of AI and computer vision technology, these robots enable surgeons to conduct complex surgeries with new levels of efficiency and accuracy. Some surgical robots might even be able to finish tasks on their own, giving surgeons the option to supervise operations from a console.
Modular Robots
Modular robots can be customized to do a variety of tasks and improve other systems. These include prosthetic robotic arms and legs and therapeutic exoskeleton robots in the field of healthcare.
Therapeutic robots can aid in the recovery process following strokes, paralysis, traumatic brain injuries, or disabilities brought on by multiple sclerosis. To help people with spinal injuries carry out daily duties, Intel and Accenture are now creating a robotic arm that can be put on a wheelchair. Robots using AI and depth cameras can measure a patient’s progress more precisely than a human eye by monitoring the degree of motion in various positions and keeping track of their form as they perform the activities that are recommended. They can communicate with patients to offer guidance and inspiration.
Autonomous Mobile Robots
Because they may help with essential requirements like telepresence, drug distribution, and disinfection while freeing up staff to spend more time with patients, AMRs are frequently used by healthcare companies. AMRs can self-navigate to patients in exam or hospital rooms when fitted with light detection and ranging (LiDAR) devices, visual compute, or mapping capabilities, enabling doctors to communicate from a distance. An AMR can accompany doctors as they perform hospital rounds if it is operated by a remote specialist or other employee. This enables the specialist to provide input via an on-screen consultation regarding patient diagnosis and management.
Also Read: 8 Best Medical Diagnosis Apps for Patients and Doctors in 2024
A prime example of an autonomous mobile is RoomieBot, an autonomous mobile robot, which assisted medical staff and practitioners by taking the temperature, blood oxygen level, and medical history of high-risk Covid-19 patients when they arrived at the hospital.
Nanomedication Application in Healthcare
Although it may still sound like science fiction, nanotechnology is steadily influencing our daily lives as one of the emerging future healthcare trends. It is perfectly reasonable to expect that 2023 will usher in a number of groundbreaking developments in the field of nanomedicine. With recent development of microscopic self-replicating robots (xenobots), the nanomedicine sector is soon to invite investors and it holds tremendous unchartered potential.
The use of nanoscale (microscopically small) materials and objects, such as biocompatible nanoparticles, nanoelectronic devices, or even nanorobots, for specific medical purposes and manipulations, such as the diagnosis or treatment of living organisms, is what is referred to as nanomedicine.
By injecting a collection of nanorobots into a human’s blood arteries, it can, for instance, be employed as a potential hunter for cancer cells or viruses.
On a cellular level, this technology is anticipated to successfully combat a wide range of hereditary, oncologic, or autoimmune illnesses, such as cancers, arthritis, and others (or even become an ultimate solution to them).
IoMT Applications in Healthcare
Even though the IoMT is not a novel concept, by 2023 this industry will experience exponential growth. There are various applications of IoMT, from wearable tech, mobile apps, to smart autonomous devices.
Mobile apps and Wearables in Healthcare
Apps for remote health monitoring and wellness will continue to grow in popularity. You may find a good number of professional (and many other semi-professional) mobile apps for healthcare and wellness in the GooglePlay or iTunes catalogs.
Some of those mobile apps have the ability to connect to wearables like pulsometers or fitness trackers to use the information gathered by the sensors attached to your body to report or evaluate your health conditions, including blood pressure, body temperature, pulse, and other metrics.
Smart & Autonomous Devices
By minimizing the tasks linked to supply management or sanitary maintenance that medical professionals must perform, autonomous nursing robots or self-moving smart gadgets can substantially assist them.
Different types of robots can work in a variety of hospital-based settings and positions, protecting human workers from infection risks or stress brought on by the extreme burden placed on many US hospitals by a COVID-19 patient overflow.

Healthcare Software Application
Any software created with the healthcare industry in mind falls under the banner of a healthcare software. A clearer definition would set this software apart from medical, where the former relates to patient care and experience and the latter to the improvement of diagnosis and treatment.
Google is a leader in healthcare technology trends (in its broad meaning), utilizing AI and big data solutions in all sectors from diagnosis to insurance.
Microsoft started Project Emma, a medical device designed to stabilize hand tremors in Parkinson’s patients, which made headlines around the world. It expanded their reach in the healthcare sector (largely on the software side), to the point where they now have a separate, multi-billion dollar facility for medical, health, and genomic research.
Amazon is also utilizing its logistics know-how in the healthcare industry. In order to serve its 647,000 employees and their families with more accessible and inexpensive healthcare, the corporation is also forming collaborations to provide software and technological solutions for the healthcare industry.
Smart Implants
In 2023, more implant-related choices and technologies will enter the healthcare market in the United States and worldwide. This promises exceptionally higher efficiency of regenerative medicine, patient rehabilitation, and a cure for many types of disabilities that have previously been considered incurable.
3D Bioprinting Technology
By the year 2027, it is anticipated that the volume of 3D bioprinting in the medical industry will surpass $6 billion. Even though 3D printing biocompatible implants is not a novel concept, in 2023 new materials and more advanced prosthetic techniques will surely make this technology more dependable and available to a wider range of patients.
In particular, it is expected that advancements in 3D bioprinting technology will improve the following areas:
- Reduce the time and cost of manufacturing implants and bionic prosthetics.
- More reasonably priced custom bionic knee, spine, skull, and hip replacements.
- Medical equipment and surgical instruments custom designed for the perfect fitting.
- New implant technologies, implant types, and implant materials are expected to function, fit better, and last longer.
- Mechanical limbs that can function fully, improved lightweight prosthetic designs, and higher levels of bone-implant integration.
- More options for 3D-printable, life-saving implants for people with neurological and cardiovascular conditions.
Neural Implants
In 2023, effective brain-computer implant products are anticipated to make their market debut. Neuralink anticipates beginning the implantation of its devices in human brains at least in 2022. Numerous businesses, groups, initiatives, and startups are preparing to offer their neuro-implants for a range of medical uses, including helping patients with various forms of paralysis or blindness regain some degree of functional independence.
It was revealed in 2021 that a team of researchers had implanted a microelectrode array into a blind person’s visual cortex, enabling her to recognize a number of letters and shapes. Although there is still a long way to go, brain implants’ potential to help people with a variety of disabilities seem to have a truly amazing and promising future.
Other examples of implants forever changing lives is the story of Neil Harbisson, who can hear colors (yes, you read that right!).
Healthcare Entities’ Data Sharing and Interoperability
Every clinic typically maintains a database with information on all of its patients. This method requires patients to undergo thorough diagnostics each time they seek out a new healthcare professional, resulting in double spending on recurrent procedures. In order to achieve interoperability, a centralized and common database that can be accessible by all clinics that provide care for a specific patient must be created. Given the interdependence of the systems in the human body, a full medical picture can lead to significantly better outcomes than a narrow set of information that only includes a few reported symptoms but not the underlying causes of health problems.
Healthcare industry trends such as interoperability initiatives are expected to reach a new level in 2023 because of strong backing from investors and the government. Healthcare systems that operate alone and refuse to exchange data with other organizations will become obsolete and less influential. For the development and expansion of open systems, cutting-edge software technologies like platform integration and APIs will be leveraged. By the end of the decade, the medical sector is anticipated to use blockchain to store patient health records.
Commercialism in the Medical Industry
The medical sector now more than ever resembles a market for goods and services. Healthcare organizations that compete with them use marketing techniques to offer their services to customers (patients). When a patient wants a certain medical service, there are many providers willing to meet their needs. The only businesses that will succeed in the long run in their fields are those that comprehend their customers and adjust to their complex needs.
Even though commercialism is one of the leading current trends in healthcare, in 2023, the consumerism tendency in healthcare is expected to intensify. Medical goods and services will be sold digitally through marketplaces and online shops. In just a few clicks, customers will be able to compare information and book medical procedures online.
On websites like Walmart and Amazon, you may already obtain medications and medical supplies made by renowned brands. In 2023, more businesses will enter the online market, offering thorough details about their prices and utilizing e-pharmacy, telehealth, and retail care.
Conclusion
These are some of the emerging healthcare trends that are expected to come into the limelight in 2023. To learn more about these technological trends in healthcare, get in touch with us at Trango Tech, the leading healthcare app development company, and we’ll build a stellar healthcare app while making sure to utilize all the rising healthcare trends, helping you reach your zenith.